 Mitochondrial
DNA: Coding Region SNP Assay Development
Mitochondrial
DNA: Coding Region SNP Assay Development
Participants: Peter M. Vallone, Michael D. Coble, Margaret C. Kline, and John M. Butler (AFDIL participants: Rebecca Just and Thomas Parsons)
Project Timeframe: 2001 to 2006
Purpose: The development of multiplex primer extension assays to probe coding region mitochondrial SNPs to help resolve common mitotypes.
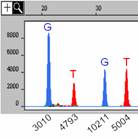
Progress: The typing of single nucleotide polymorphisms
(SNPs) located throughout the mitochondrial genome (mtGenome) allows for
differentiation between individuals possessing an identical HV1/HV2
sequence. A set of 11 SNPs selected for
distinguishing individuals of the most common Caucasian HV1/HV2 mitotype were
incorporated in an allele-specific primer extension assay. The 11-plex assay probed SNPs located at
positions 477, 3010, 4580, 4793, 5004, 7028, 7202, 10211, 12858, 14470 and
16519 in the mtGenome. The assay was
optimized for multiplex detection of these SNPs. Primers were designed to allow for the simultaneous polymerase
chain reaction (PCR) amplification of 11 unique regions in the mtGenome. Locus specific primers of varying lengths
were employed in multiplex primer extension reactions. Extension primers binding 5’ adjacent to the
SNP site of interest were enzymatically extended using fluorescently labeled
dideoxynucleotides (ddNTPs). Resolution
and detection of each extended fragment were achieved by analysis on a
capillary-based electrophoresis (CE) platform.
The electrophoretic mobility for the extension primers was compared in
denaturing POP4 and POP6 CE running buffers.
Empirical adjustment of extension primer concentrations resulted in even
signal intensity for the 11 loci probed.
The development of the mtSNP 11-plex assay has resulted in an accurate
method for typing sequence variant mtSNPs on a platform common to forensic
laboratories.
Publications or Presentations Resulting From This Project:
Coble, M.D., Vallone, P.M., Just, R.S., Diegoli, T.M., Smith, B.C., Parsons, T.J. (2006) Effective strategies for forensic analysis in the mitochondrial DNA coding region. Int. J. Legal. Med. 120:27-32. [Supplementary Data].
Kline, M.C.,
Vallone, P.M., Redman, J.W., Duewer, D.L., Calloway, C.D., and Butler, J.M.
(2005) Mitochondrial DNA typing screens with control region and coding region
SNPs.
J.
Forensic Sci. 50(2): 377-385.
Just, R.S., Irwin, J.A., O'Callaghan, J.E., Saunier, J.L., Coble, M.D.,
Vallone, P.M., Butler, J.M., Barritt, S.M., and Parsons, T.J. (2004) Toward
increased utility of mtDNA in forensic identifications.
Forensic
Sci. Int. 146S: S147-S149.
Vallone, P.M., Just, R.S., Coble, M.D., Butler,
J.M., and Parsons, T.J. (2004) A multiplex allele-specific primer extension
assay for forensically informative SNPs distributed throughout the
mitochondrial genome.
Int.
J. Legal Med. 118: 147-157.
Coble, M.D., Just, R.S., O'Callaghan, J.E., Letmanyi, I.H., Peterson, C.T., Irwin, J.A., Parsons, T.J. (2004) Single nucleotide polymorphisms over the entire mtDNA genome that increase the power of forensic testing in Caucasians. Int. J. Legal Med. 118: 137-146.
[Return to NIJ Projects page] [Return to STRBase]
Last updated: 06/27/2007
Disclaimer: This project was supported by National Institute of Justice Grant Number 2003-IJ-R-029, which is an interagency agreement between NIJ and the NIST Office of Law Enforcement Standards, awarded by the National Institute of Justice, Office of Justice Programs, US Department of Justice. Points of view in this document are those of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official position or policies of the US Department of Justice. Certain commercial equipment, instruments and materials are identified in order to specify experimental procedures as completely as possible. In no case does such identification imply a recommendation or endorsement by the National Institute of Standards and Technology nor does it imply that any of the materials, instruments or equipment identified are necessarily the best available for the purpose.